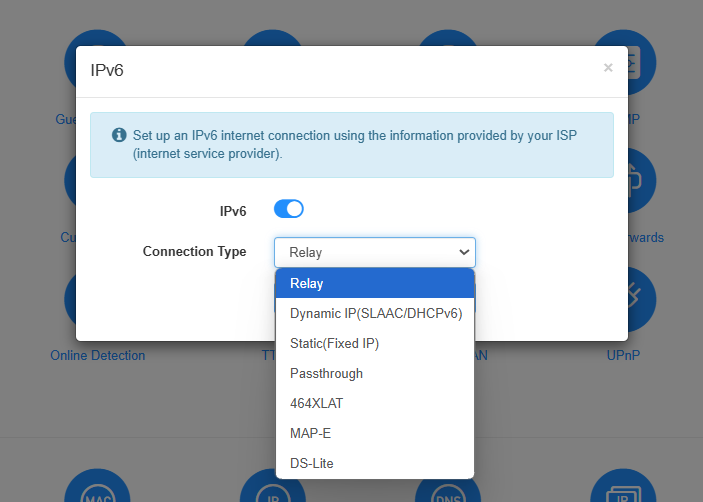
IPv6¶
IPv6 may not be supported in the current version of the firewall, VPN, block list, etc.Therefore, the IPv6 function can only be used for configuration on this interface. There are 7 types of IPv6 Internet connection, including Relay, Dynamic IP(SLAAC/DHCPv6), Static (Fixed lP), Passthrough, 464XLAT, MAP-E, and DS-Lite. Please choose the appropriate one and configure the parameters according to your ISP.
Note
- If the current version of the firewall (or VPN, block list, and etc.) does not support IPv6, you may enable and configure the IPv6 function on this page.
- If you use VPN and IPv6 functions at the same time, it's likely to cause IPv6 data leakage.
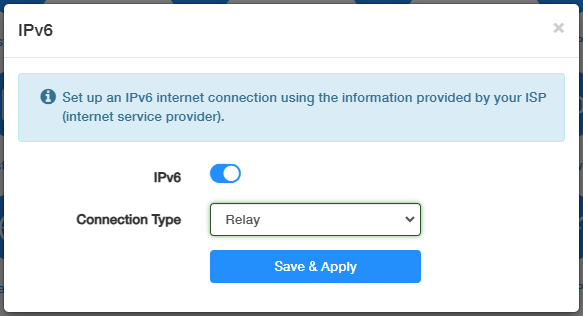
Relay¶
Relay is typically used for IPv6 transition mechanisms. The router will act as a relay between your local IPv6 network and an IPv4-based upstream network provided by your ISP.
Select Relay and just click Save & Apply without any additional configuration.
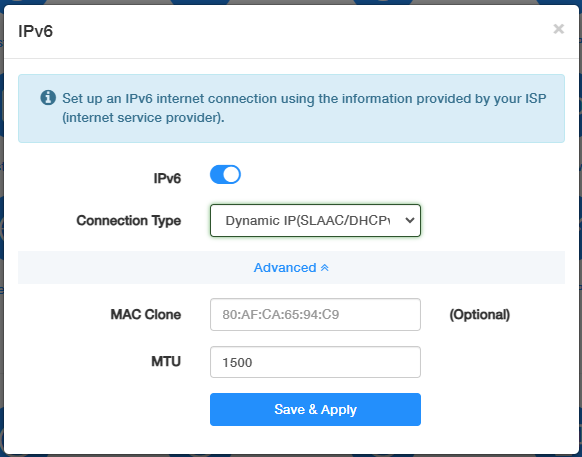
Dynamic IP(SLAAC/DHCPv6)¶
Select Dynamic IP(SLAAC/DHCPv6), and configure MAC Clone and MTU as needed.Then click Save & Apply.
- MAC Clone: (Optional) Enter the MAC address of the device that is allowed by your ISP. You can usually find this in the device's network settings or on a label on the device.
- MTU: Enter the appropriate MTU size (commonly 1500 bytes for compatibility with IPv4).
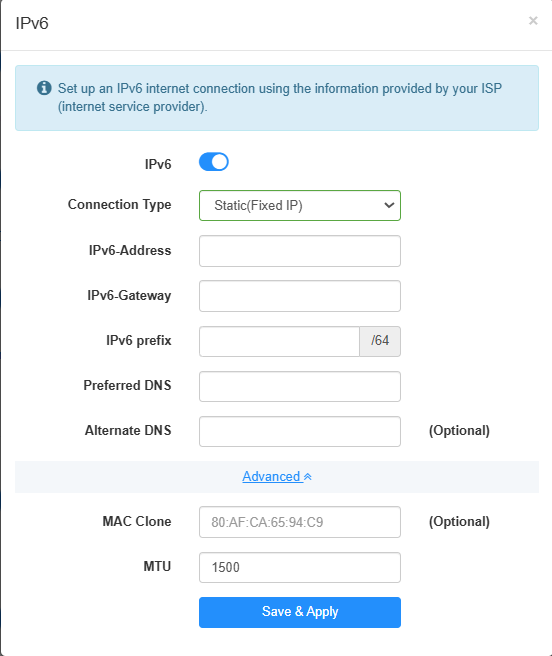
Static(Fixed lP):¶
Select Static (Fixed IP) and enter the fixed IPv6 address, gateway, prefix and DNS server address provided by your ISP. Then click Save & Apply.
- MAC Clone: (Optional) Enter the MAC address of the device if the ISP requires a specific MAC address for the static IP assignment. You can usually find this in the device's network settings or on a label on the device.
- MTU: Enter the appropriate MTU size based on the network's physical layer, typically 1500 bytes for Ethernet.
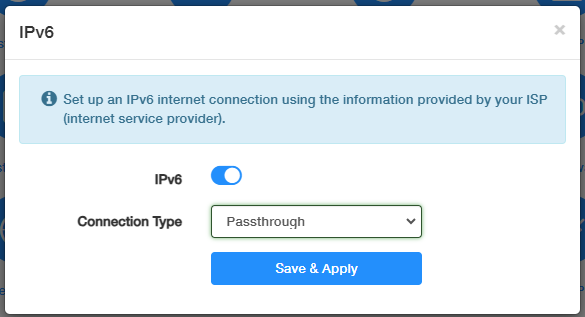
Passthrough¶
Passthrough allows an IPv6-enabled device to manage its own IP settings directly from the ISP, bypassing the router's DHCP server.
Select Passthrough and just click Save & Apply without any additional configuration.
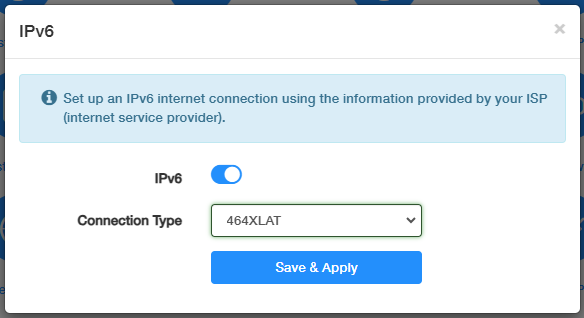
464XLAT¶
464XLAT is a stateless translation mechanism that allows IPv4-only devices to communicate over an IPv6 network.
Select 464XLAT and just click Save & Apply without any additional configuration.
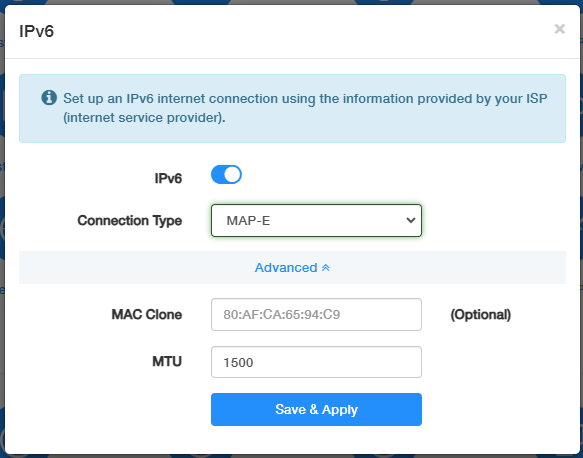
MAP-E¶
MAP-E (Mapping of Address and Port with Encapsulation) is a method for translating IPv6 addresses to IPv4 addresses.
Select MAP-E, and configure MAC Clone and MTU as needed. Then click Save & Apply.
- MAC Clone: (Optional) MAP-E usually does not involve MAC address restrictions, so MAC Clone is not typically necessary.
- MTU: Enter the appropriate MTU size according to the maximum IPv4 packet size, which is typically 1500 bytes minus the headers.
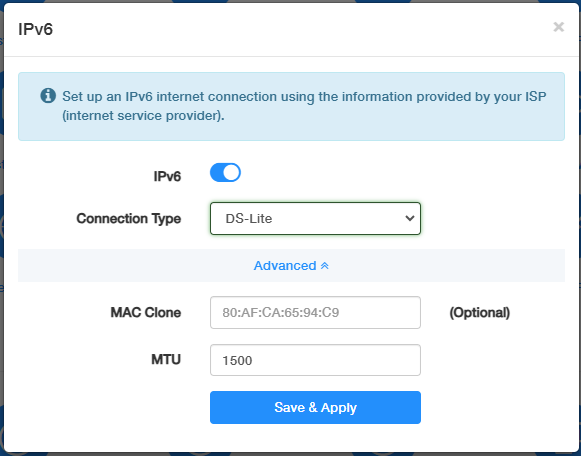
DS-Lite¶
DS-Lite (Dual-Stack Lite) is a technology that allows ISPs to provide IPv4 service over an IPv6 network.
Select DS-Lite, and configure MAC Clone and MTU as needed. Then click Save & Apply.
- MAC Clone: (Optional) DS-Lite usually does not involve MAC address restrictions, so MAC Clone is not typically necessary.
- MTU: Enter the MTU value based on your network's requirements. The value should be within the range of 1280 to 1582 bytes. The MTU setting is important to ensure that the encapsulated IPv4 packets can be transmitted over the IPv6 network without fragmentation.