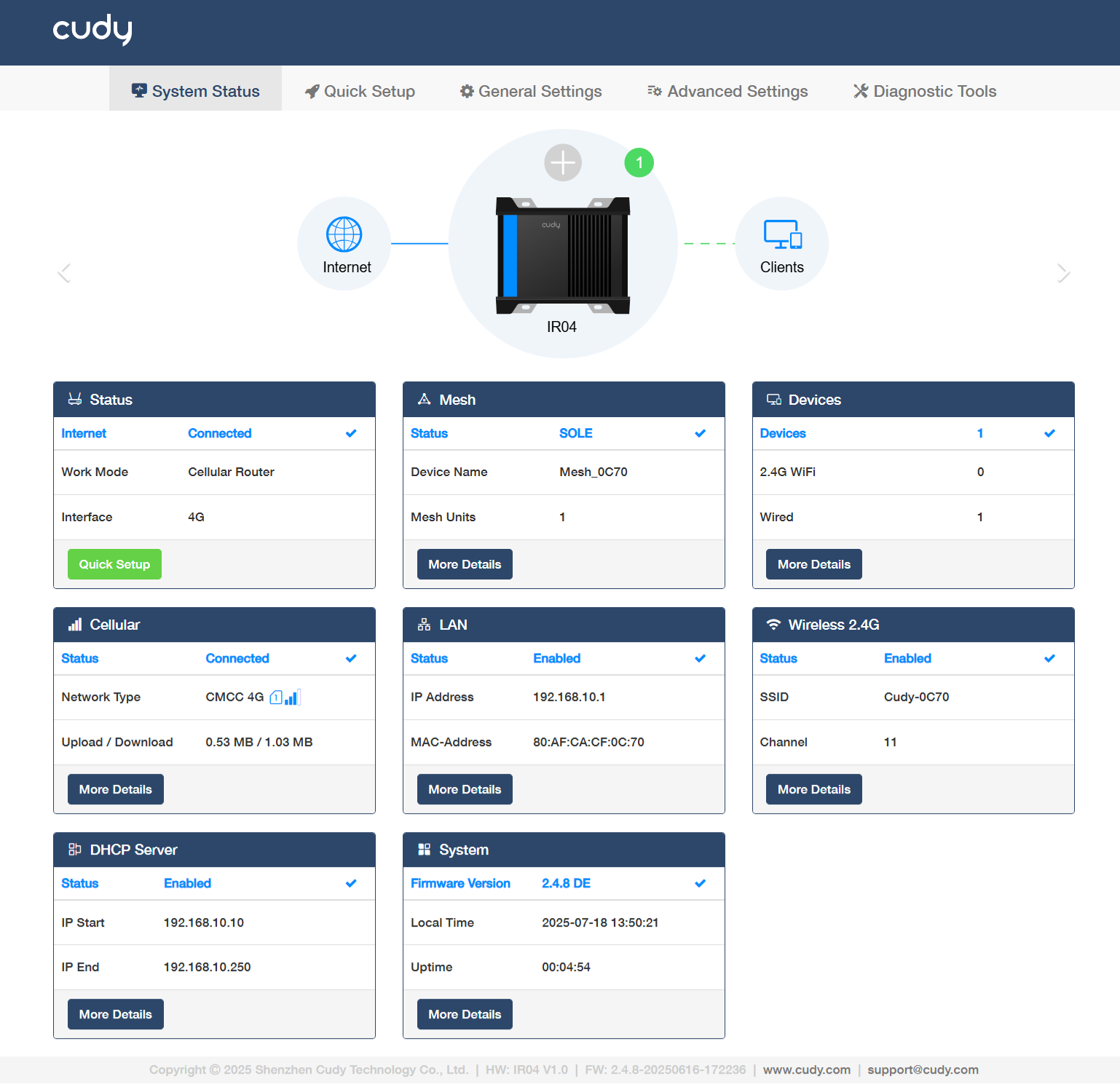
System Status¶
Status¶
shows whether the router has connected to the Internet or not, and its work mode and interface. Click Quick Setup to redirect to the Quick Setup.
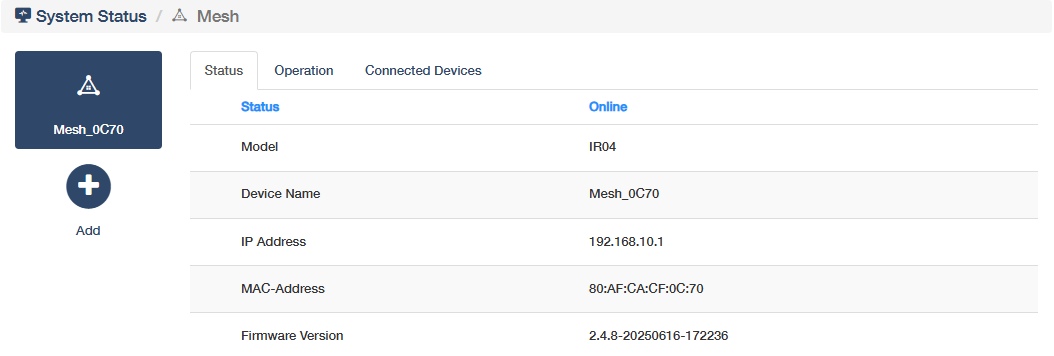
Mesh¶
shows the router’s Mesh network status (SOLE or MESH), the mesh device name and the amount of mesh units. Click More Details to know more or configure some settings (refer to Mesh).
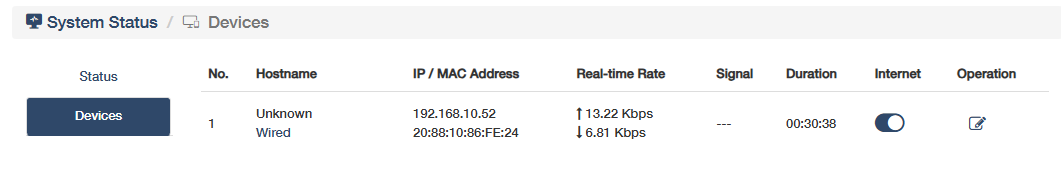
Devices¶
shows the amount of devices connected to this router, and the connection method being 2.4G WiFi or Wired; while the Mesh device will be not be displayed here but on the More Details -> Status page.
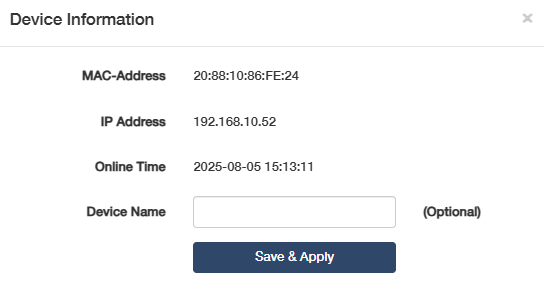
- View the Device information about hostname, IP/MAC address, real-time rate, Signal and connection duration.
- Enable or disable the Internet connection.
- Edit the device name by clicking on the Operation.
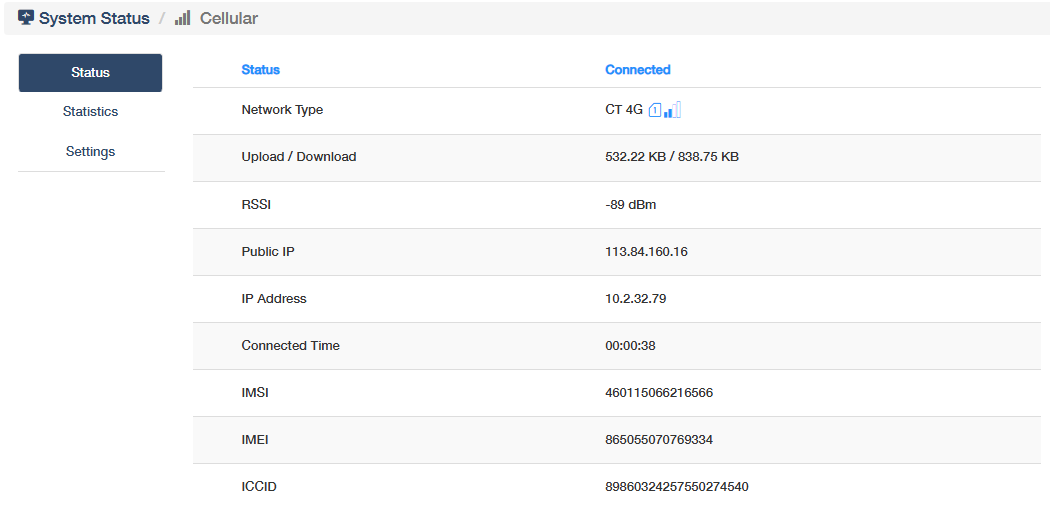
Cellular¶
shows whether the router has connected to the cellular network, its network type and upload/download rate. Click More Details to know more information on the Status and Statistics sub-pages, or configure some settings (refer to Cellular).
Status
- Network Type: The cellular technology standard in use (e.g., LTE, 5G).
- Upload/Download: Data transfer speeds for sending/receiving data.
- RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator, reflecting signal quality (closer to 0 is stronger).
- Public IP: The external IP address assigned by the carrier for internet communication.
- IP Address: The local/internal IP of the router within the cellular network.
- Connected Time: Duration since the router established the cellular connection.
- IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity, unique subscriber identity stored in the SIM card.
- IMEI: International Mobile Equipment Identity, unique hardware identifier for the router.
- ICCID: Integrated Circuit Card Identifier, SIM card serial number.
- Mode: Current operational mode.
- MCC/MNC: Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code, identifying the carrier/country.
- Cell ID/PCID: Cell ID is Physical cell tower identifier, and PCID physical cell identity.
- Band/UL Bandwidth: Frequency band and uplink bandwidth for data transmission.
- DL Bandwidth: Downlink bandwidth allocated by the carrier for receiving data.
- RSRP: Reference Signal Received Power, Average power of LTE/5G reference signals.
- RSRQ: Reference Signal Received Quality, Signal quality ratio of RSRP to total interference/noise.
- SINR: Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio, Measures signal purity by comparing useful signal to interference/noise.
- CSQ: Command Signal Quality, Legacy metric for signal strength (0–31 scale), often used in 2G/3G.
Statistics
- Current Traffic:Real-time data usage of the active cellular connection, to monitor immediate bandwidth consumption to detect anomalies.
- Monthly Traffic: Cumulative data usage within the current billing cycle, critical for cost control in metered plans.
- Total Traffic: Lifetime data transmitted/received since the router was deployed or reset. Long-term usage analysis for capacity planning and maintenance scheduling.
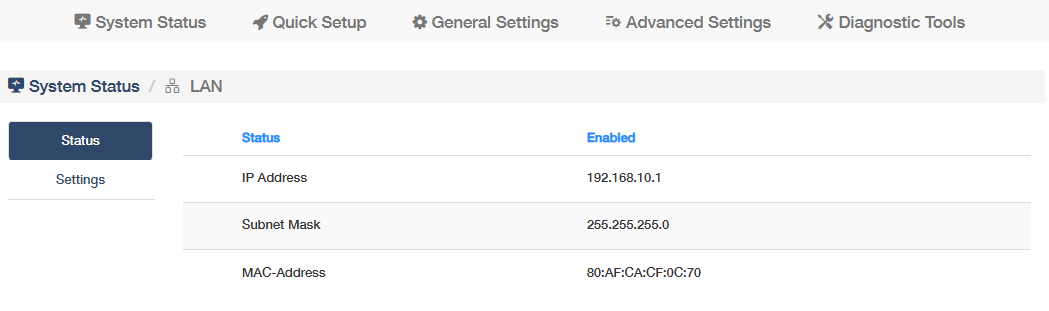
LAN¶
shows whether the router's LAN network connection is enabled or not, its IP address and MAC address. Click More Details to know more information on the Status sub-page, or configure some settings (refer to LAN).
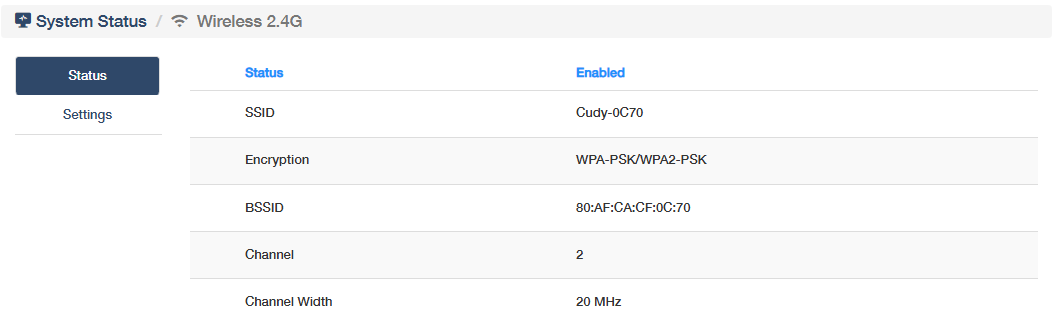
Wireless 2.4G¶
shows whether ther router's Wireless 2.4G network is enabled or not, its SSID and channel. Click More Details to know more information on the Status sub-page, or configure some settings (refer to Wireless 2.4G).
- Status: Indicates whether the 2.4GHz wireless radio is active or inactive.
- SSID: Service Set Identifier, the visible name of the wireless network.
- Encryption: Security protocol used to protect data transmission.
- BSSID: Basic Service Set Identifier, the MAC address of the router’s 2.4GHz radio, uniquely identifying its hardware.
- Channel: The frequency band number selected for wireless communication.
- Channel Width: Bandwidth allocated, wider channels offer higher speed but may increase interference.
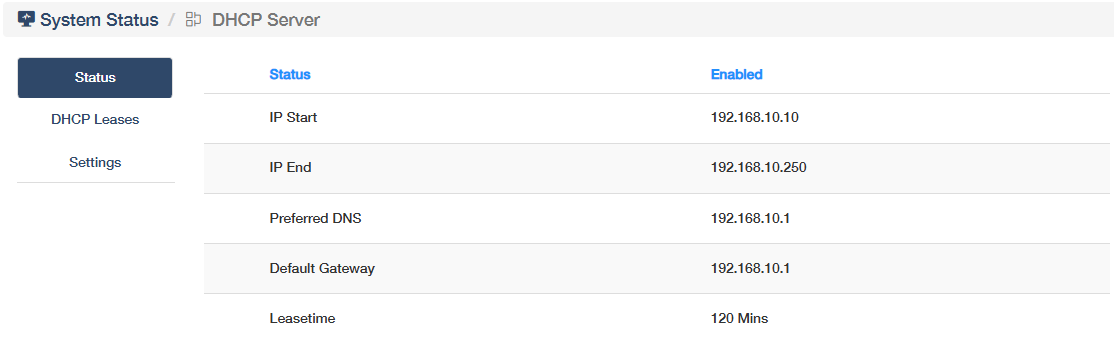
DHCP Server¶
shows whether the DHCP Server is enabled or not, and its starting/ending IP. Click More Details to know more information on the Status and DHCP Leases sub-pages, or configure some settings (refer to DHCP Server).
- Status: Indicates whether the DHCP server is active or inactive for automatic IP assignment.
- IP Start/IP End: Defines the range of IP addresses the DHCP server can assign to connected devices.
- Preferred DNS: The primary DNS server address provided to clients for domain name resolution.
- Default Gateway: The router’s IP address used as the exit point for client devices to access external networks.
- Lease Time: Duration an assigned IP address remains valid before renewal is required.
System¶
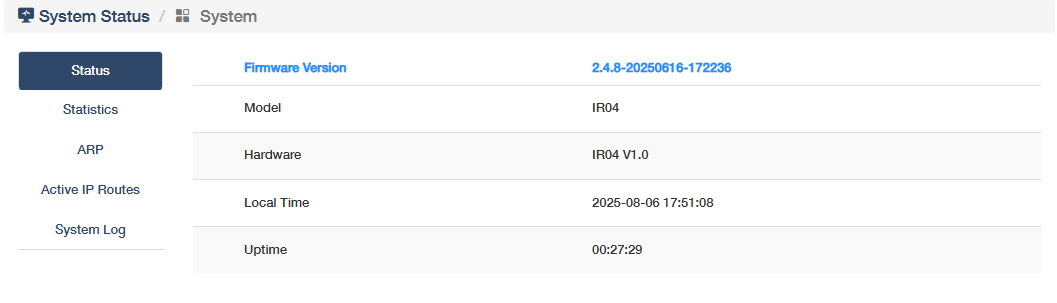
shows the router's firmware version, current local time and uptime. Click More Details to know more information on the Status, Statistics, ARP, Active IP Routes and System Log sub-pages.
Status displays real-time operational states to provide a snapshot of system health and configuration baseline for troubleshooting.
- Firmware Version: The current software version installed on the router, critical for updates and compatibility.
- Model: The router’s product model, used for identifying hardware specifications.
- Hardware: Physical components/revision, indicating the device’s internal build.
- Local Time: The router’s configured time, essential for time-based operations and logs.
- Uptime: Duration since the last reboot, reflecting system stability and reliability.
Statistics tracks network performance metrics per interface (WLAN/LAN/Cellular) to identify bandwidth bottlenecks, packet loss, or hardware faults.
- Interface: The network port or connection type being monitored.
- Tx Bytes: Total data transmitted.
- Tx Pkts: Number of packets sent.
- Tx Errs: Transmission errors.
- Tx Drop: Packets dropped due to congestion or faults.
- Rx Bytes: Total data received.
- Rx Pkts: Number of packets received.
- Rx Errs: Reception errors.
- Rx Drop: Packets dropped during reception.
ARP maps IP addresses to MAC addresses for local network communication to detect IP conflicts and monitors connected devices in the LAN.
- IP Address: The network-layer address assigned to a device in the local network.
- MAC-Address: The physical hardware address uniquely identifying a device at the data-link layer.
- Hostname: The human-readable name assigned to the device for easier identification.
Active IP Routes shows path selection rules for data forwarding to optimize traffic routing and diagnoses connectivity issues between networks.
- Network/Target: The destination network address that the route applies to.
- Gateway: The next-hop IP address used to reach the target network.
- Metric: A numerical value indicating route priority (lower=preferred), calculated from hop count/bandwidth.
- Table: The routing table type where this route is stored.
- Interface: The physical/virtual port used for this route's traffic.
System Log records timestamped system events, errors, and operational messages for diagnostics and auditing.