Serial Service¶
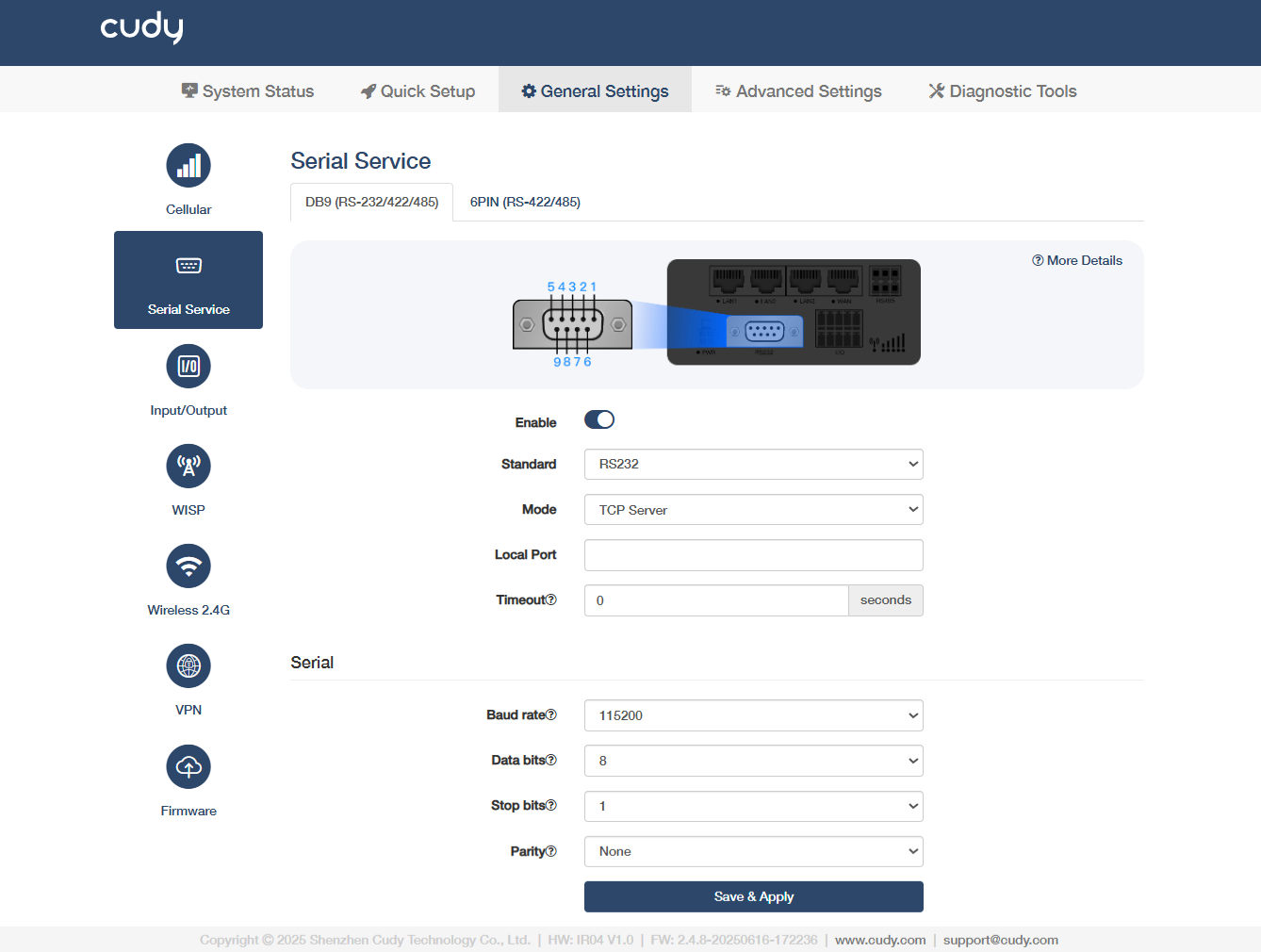
DB9(RS-232/422/485)¶
- Enable: Activate the serial interface for communication.
-
Standard: Select a specific protocol type for electrical signaling.
- RS232 uses single-ended signaling (point-to-point, <15m).
- RS422 employs differential signaling (1 driver → 10 receivers, 1200m).
- RS485-4 supports 4-wire full-duplex with dedicated TX/RX pairs.
- RS485-2 uses 2-wire half-duplex for multi-drop networks (32+ devices).
-
Mode: Select the mode accordingly.
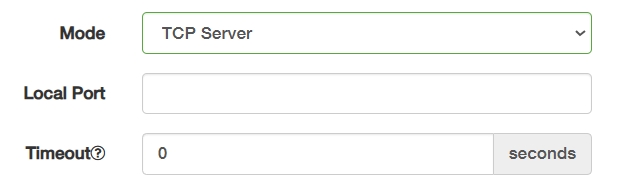
① TCP Server is a passive endpoint that listens for incoming TCP connections.
- Local Port: Enter the listening port (e.g., 5020) for accepting incoming TCP connections. Configurable, but avoid well-known ports like 80.
- Timeout: Specify a duration in seconds (0-1000) before a connection is closed due to inactivity. 0 means no timeout.
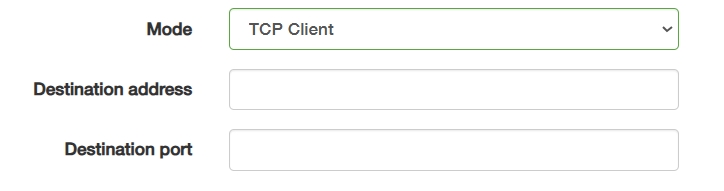
② TCP Client initiates active TCP connections to servers.
- Destination address: Enter a fixed target IP/domain (e.g., 192.168.1.100) for reliable endpoint connection.
- Destination port: Enter a predefined service port requiring handshake.
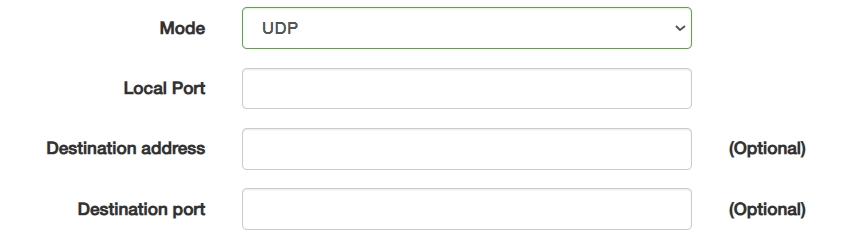
③ UDP is a connectionless protocol for low-latency broadcast/multicast.
- Local Port: Enter a dynamic/static port bound for sending/receiving datagrams (e.g., 1234 for sensor broadcasts).
- Destination address (Optional): Enter a dynamic/broadcast IP (e.g., 255.255.255.255).
- Destination port (Optional): Enter a flexible port binding without verification (e.g., 1234 for sensor broadcasts).
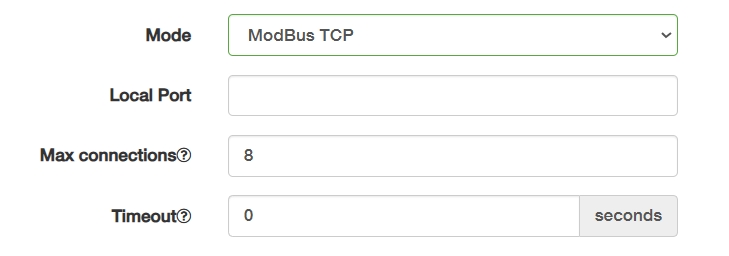
④ ModBus TCP is an industrial protocol (Layer 7) using TCP/IP for device control.
- Local Port: Fixed to 502 by default for protocol compliance. Non-standard ports may break interoperability.
- Max connections: Enter a number (1-128) to limit clients that can connect at the same time.
- Timeout: Enter the maximum wait time for slave device responses.
-
Baud rate: Select to define the speed of data transmission for serial communication, measured in bits per second (bps).
- Data bits: Select to define the number of bits (typically 5-8) used to represent each character in serial communication.
- Stop bits: Specify how many stop bits are used to mark the end of each byte in serial communication.
-
Parity: Set how the system checks for errors in data transmission by adding an extra bit to each data frame.
- None disables parity checking.
- Even makes the total 1s count even (including parity bit).
- Odd enables single-bit-error detection just like Even parity, but it demands an extra signal transition. Industrial systems often prefer Odd for better noise immunity.
-
Termination Resistor: Enable to activate the 120Ω termination resistor. Recommended for use at the bus end of RS422/RS485 to reduce signal reflections.
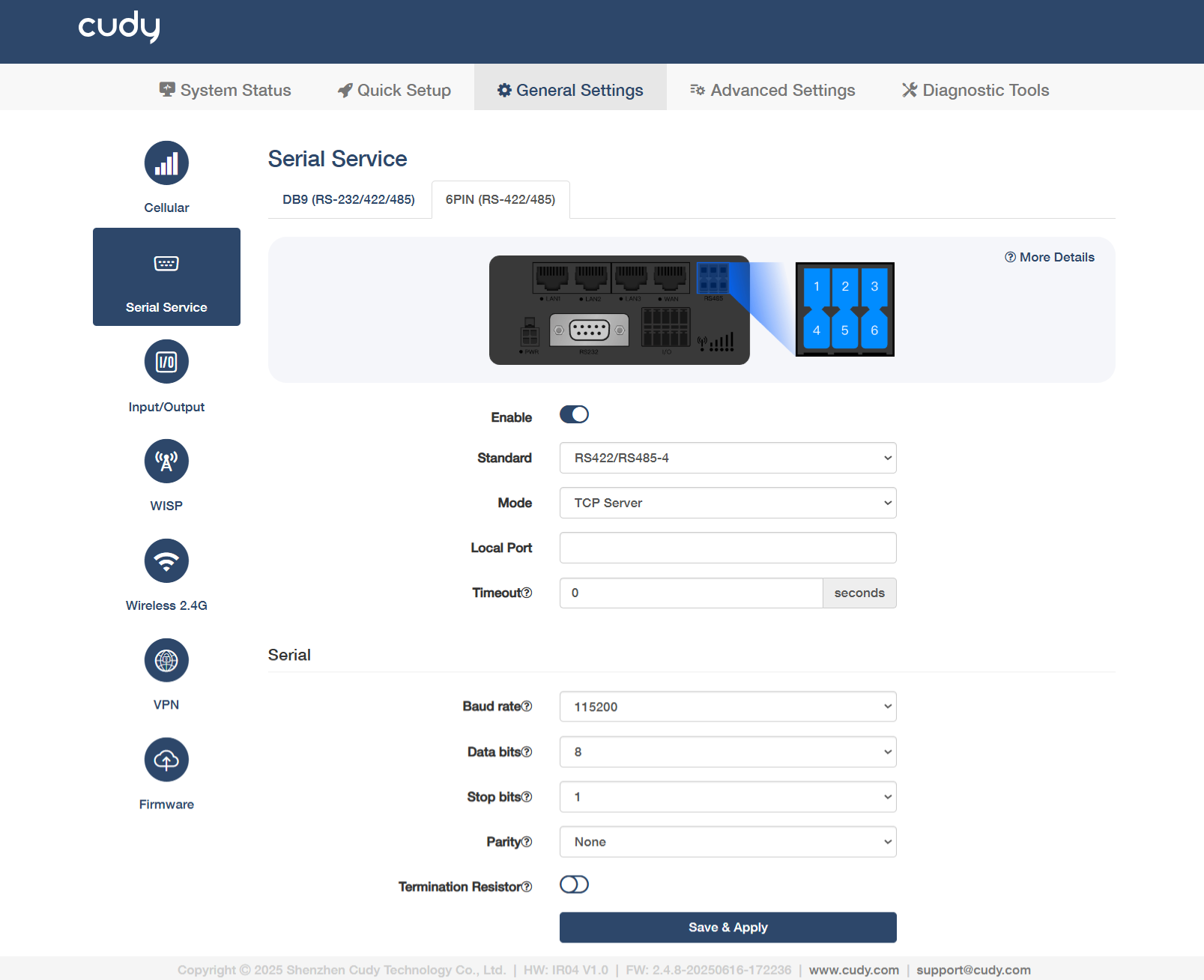
6PIN(RS-422/485)¶
- Enable: Activate the serial interface for communication.
-
Standard: Select a specific protocol type for electrical signaling.
- RS422: Differential signaling (1 driver → 10 receivers, up to 1200m).
- RS485-4: 4-wire full-duplex with dedicated TX/RX pairs.
- RS485-2: 2-wire half-duplex for multi-drop networks (32+ devices).
-
Mode: Select the mode accordingly.
① TCP Server is a passive endpoint that listens for incoming TCP connections.
- Local Port: Enter the listening port (e.g., 5020) for accepting incoming TCP connections. Configurable, but avoid well-known ports like 80.
- Timeout: Specify a duration in seconds (0-1000) before a connection is closed due to inactivity. 0 means no timeout.
② TCP Client initiates active TCP connections to servers.
- Destination address: Enter a fixed target IP/domain (e.g., 192.168.1.100) for reliable endpoint connection.
- Destination port: Enter a remote service port.
③ UDP is a connectionless protocol for low-latency broadcast/multicast.
- Local Port: Enter a dynamic/static port bound for sending/receiving datagrams (e.g., 1234 for sensor broadcasts).
- Destination address (Optional): Enter a dynamic/broadcast IP (e.g., 255.255.255.255).
- Destination port (Optional): Enter a flexible port binding without verification (e.g., 1234 for sensor broadcasts).
④ ModBus TCP is an industrial protocol (Layer 7) using TCP/IP for device control.
- Local Port: Enter a port fixed to 502 by default for protocol compliance.
- Max connections: Enter a number (1-128) to limit clients that can connect at the same time.
- Timeout: Enter the maximum wait time for slave device responses.
-
Baud rate: Select to define the speed of data transmission for serial communication, measured in bits per second (bps).
- Data bits: Select to define the number of bits (typically 5-8) used to represent each character in serial communication.
- Stop bits: Specify how many stop bits are used to mark the end of each byte in serial communication.
-
Parity: Set how the system checks for errors in data transmission by adding an extra bit to each data frame.
- None disables parity checking.
- Even makes the total 1s count even (including parity bit).
- Odd enables single-bit-error detection just like Even parity, but it demands an extra signal transition. Industrial systems often prefer Odd for better noise immunity.
-
Termination Resistor: Enable to activate the 120Ω termination resistor. Recommended for use at the bus end of RS422/RS485 to reduce signal reflections.