Input/Output¶
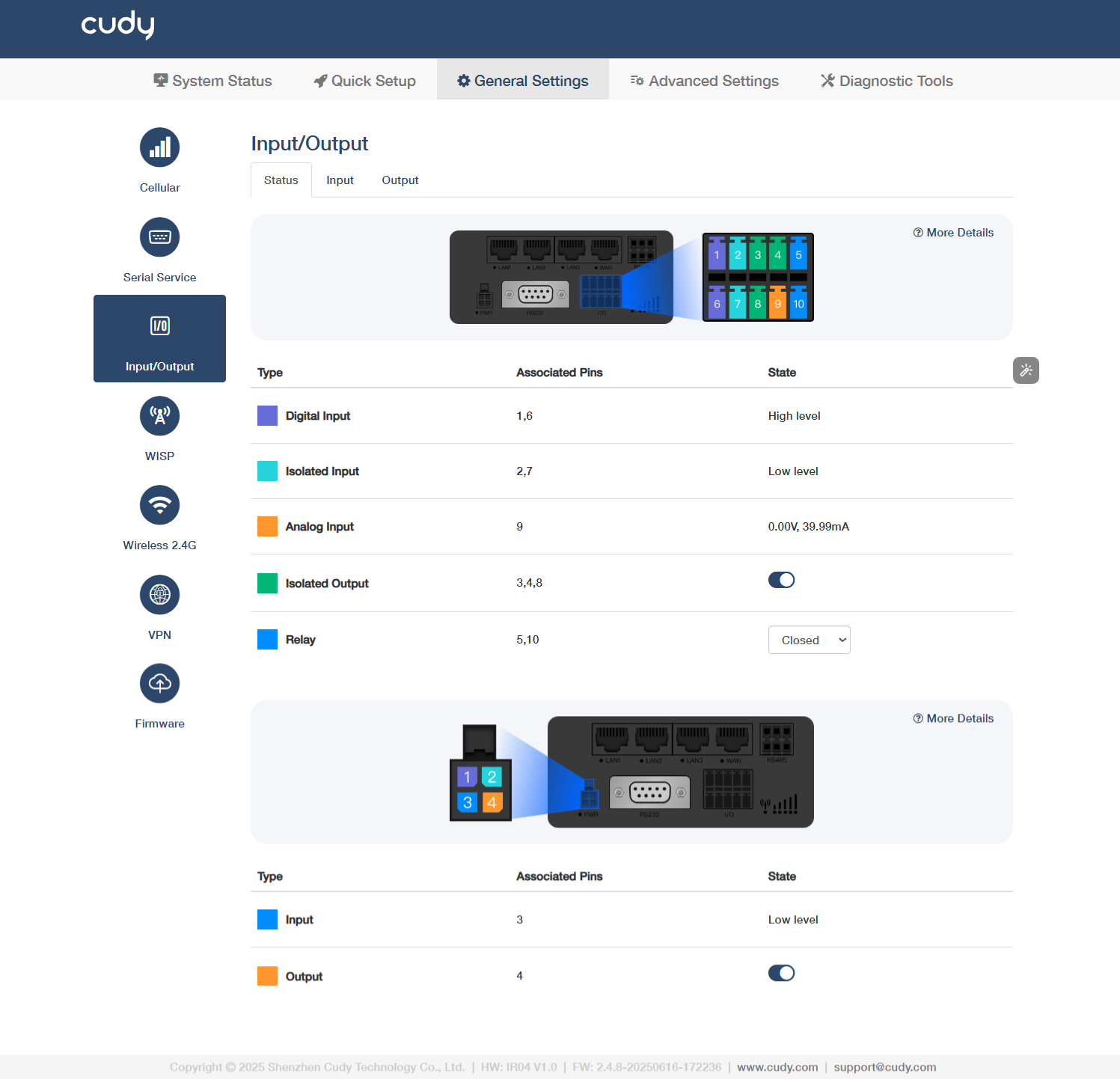
Status¶
I/O¶
-
Digital Input (Associated Pin 1/6): Detects high-level signals (e.g., 24V) for equipment status monitoring (limit switches/sensors).
-
Isolated Input (Associated Pin 2/7): Reads low-level signals (0V) with galvanic isolation (≥1500V) for safety interlock/emergency stops.
-
Analog Input (Associated Pin 9): Supports 0-10V/4-20mA signals for precision measurement (temperature/pressure transmitters).
-
Isolated Output (Associated Pin 3/4/8): Transistor outputs (On=0V, Off=high-Z) for driving relays/solenoids (≤0.5A load).
-
Relay (Associated Pin 5/10): Electrically isolates control circuits from power circuits (e.g., 5V PLC → 240V motor). Select Closed (NO) when energized (current flows to load) or Open (NC) when de-energized (failsafe/default state).
![]() Use ferrite beads on analog wires to suppress EMI in noisy environments.
Use ferrite beads on analog wires to suppress EMI in noisy environments.
PWR¶
-
Input (Associated Pin 3): Receives external power to activate the device.
◦ High Level (Typ. 24V±10%): Normal power reception, device operational
◦ Low Level (<1V): Power loss/undervoltage (check wiring/supply voltage)
◦ Floating: Open circuit (verify terminal connection integrity)
-
Output (Associated Pin 4): Supplies regulated power to connected peripherals.
◦ On: Actively supplying power to peripherals (e.g., 24V/5V output enabled)
◦ Off: Output disabled (manual shutdown or protection triggered)
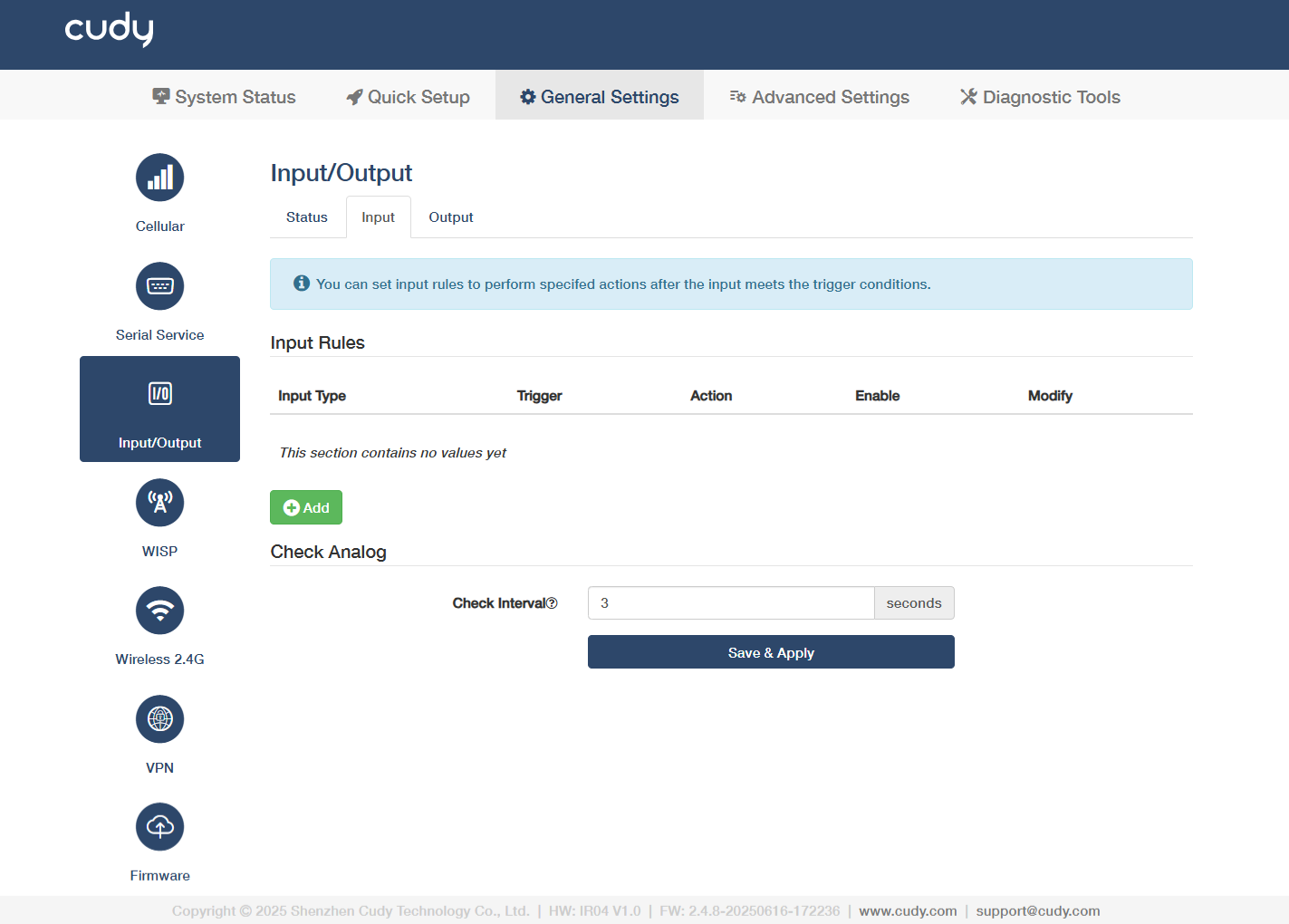
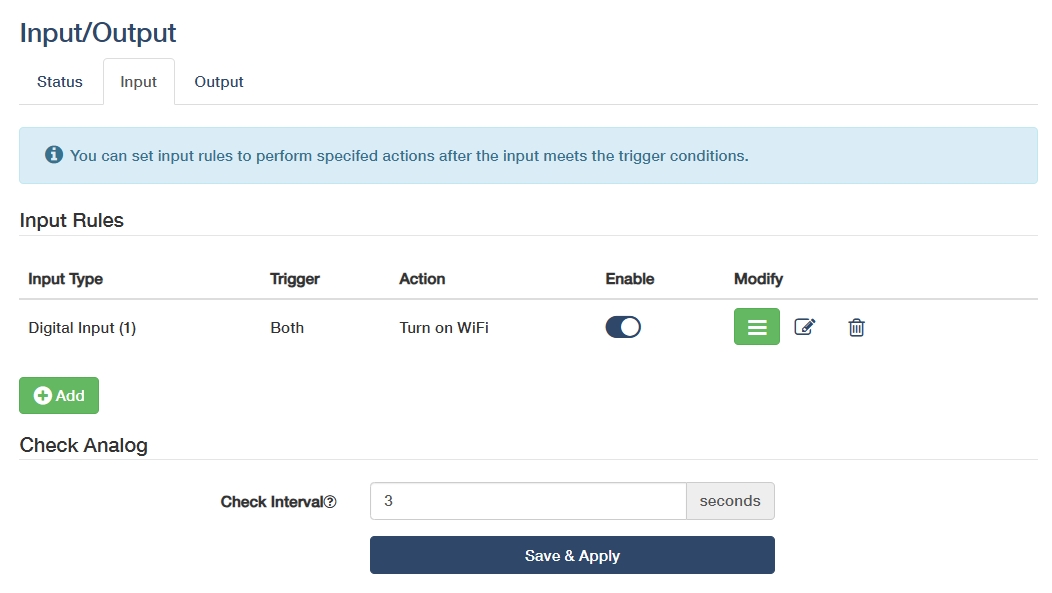
Input¶
- Add: Click to configure input rules to perform specified actions after the input meets the trigger conditions.
- Enable: Enable this entry of input rule.
-
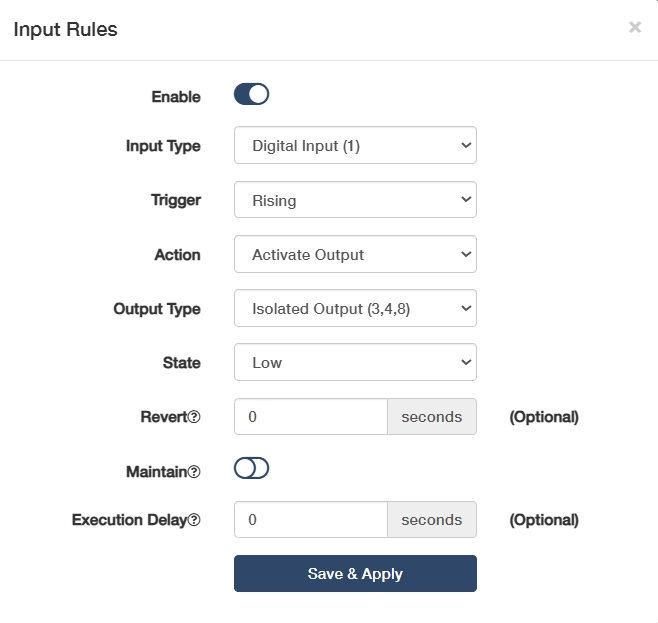
Input Type: Select to define the signal category (e.g., digital/analog/pulse).
◦ Digital Input(1): Standard binary input for detecting 24V signals.
◦ Isolated Input(2,7): Galvanically separated input for safety-critical signal.
◦ Digital Input(Power Socket 3): Power-monitoring input, detecting mains voltage presence via socket status.
◦ Analog Input(6,9): Reads 0-10V/4-20mA signals for precision measurement.
-
Trigger: Select a condition to activate the rule.
◦ For Digital/Isolated Input: Rising triggers when signal transitions from low to high, ideal for power-on events; Falling triggers when signal transitions from high to low, used for emergency stop detection; Both responds to any voltage change, perfect for pulse counting or state monitoring.
◦ For Analog Input: Inside Range triggers when the signal stays between Min/Max values; Outside Range triggers when the signal exceeds Min/Max thresholds.
-
Analog Type (for Analog Input): Select to match your sensor's output signal type. Current (mA) is used for 4-20mA/0-20mA industrial sensors (like pressure transmitters) as it’s resistant to signal degradation over long distances; Voltage (V) is used for 0-10V/±10V signals (like position sensors) with simpler wiring but shorter effective range due to voltage drop.
- Minimum (V) / Maximum (V) (for Analog Input): Set voltage thresholds to define the valid range for voltage-based triggers.
-
Minimum (mA) / Maximum (mA) (for Analog Input): Configure current limits for current-loop device monitoring.
-
Action: Operation to execute when the rule is triggered.
◦ Activate Output: Triggers a designated output port. Then select a target Output Type and current input State, enter a Revert interval to determine auto-reset after trigger ends; enable or disable Maintain to decide lock state until manual reset.
◦ Send SMS: Send alert messages via cellular module, which requires configured GSM/GPRS parameters. Edit the SMS Text as needed, add the Phone number to send your SMS.
◦ SIM Switch: Automatically fails over to the selected backup SIM card when primary cellular signal is lost. Recommended to keep it Auto.
◦ Turn on WiFi: Enables the router's WiFi for wireless client connections.
◦ Turn off WiFi: Disables WiFi to conserve power or enhance security.
◦ Reboot: Restart the system to apply configurations or recover from faults.
-
Execution Delay:(Optional) Enter the time when will the action be executed after the rule being triggered.
-
Check Interval: Enter an interval in seconds to check analog input value.
-
Save & Apply: Click to save and activate the new settings or changes.
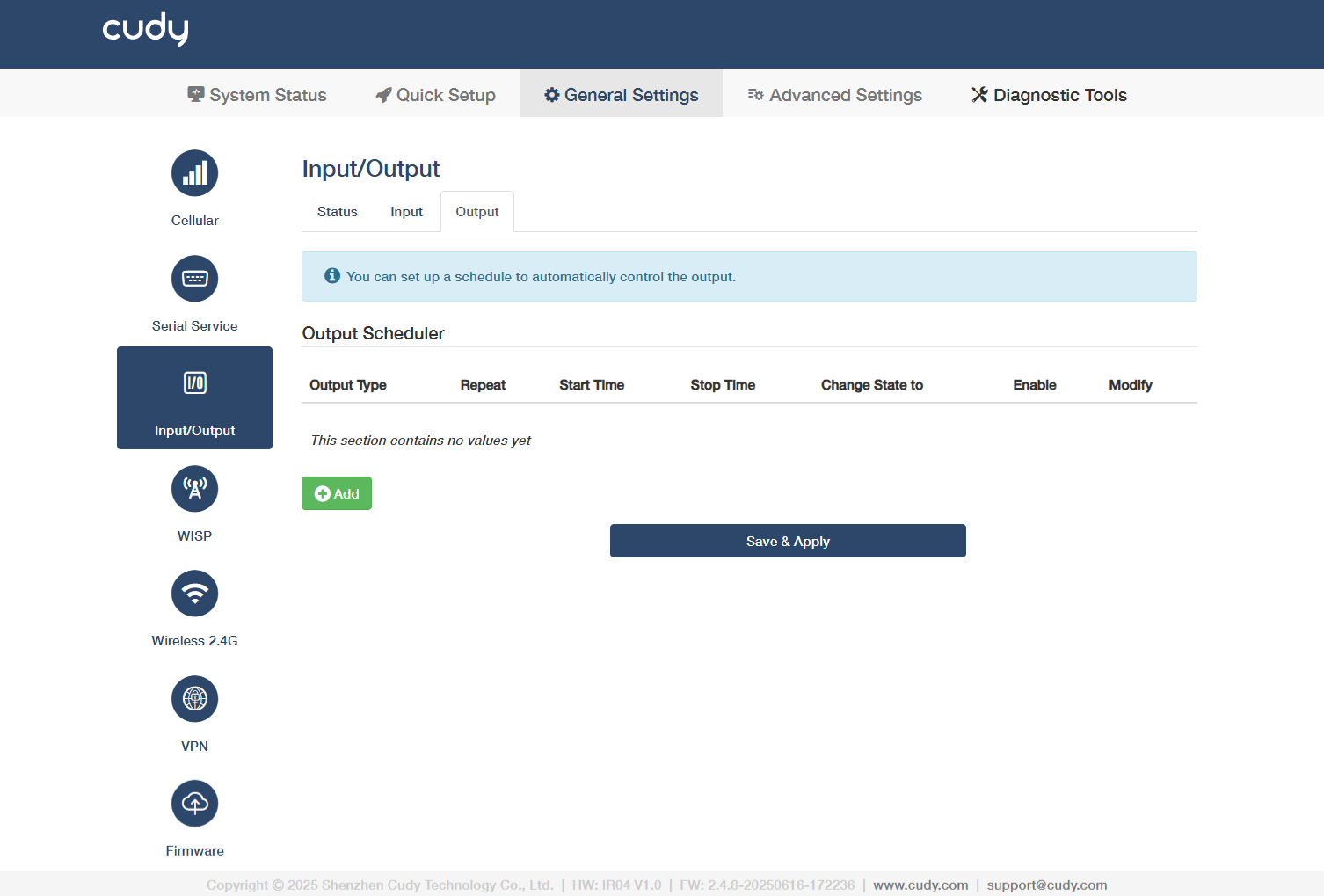
Output¶
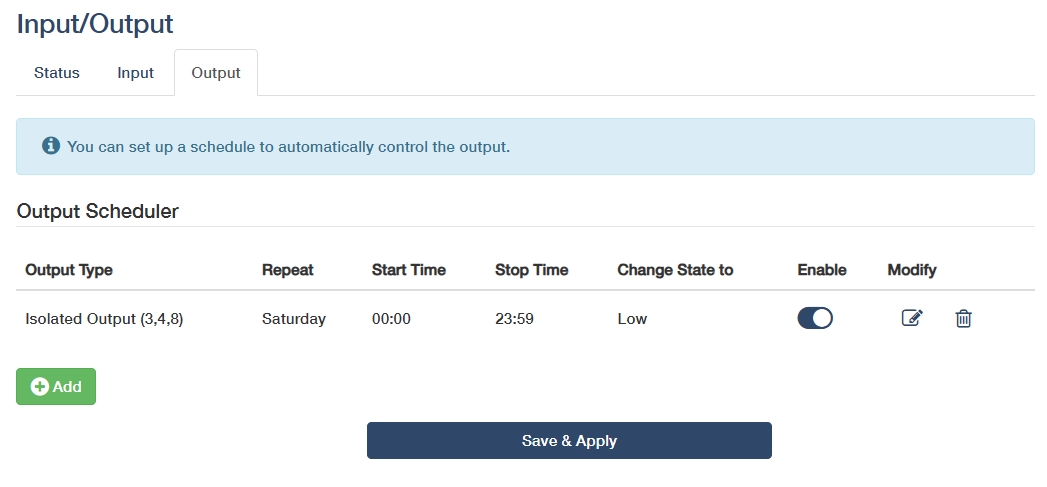
- Add: Click to configure output scheduler to perform specified actions after the input meets the trigger conditions.
- Enable: Enable this entry of output scheduler.
-
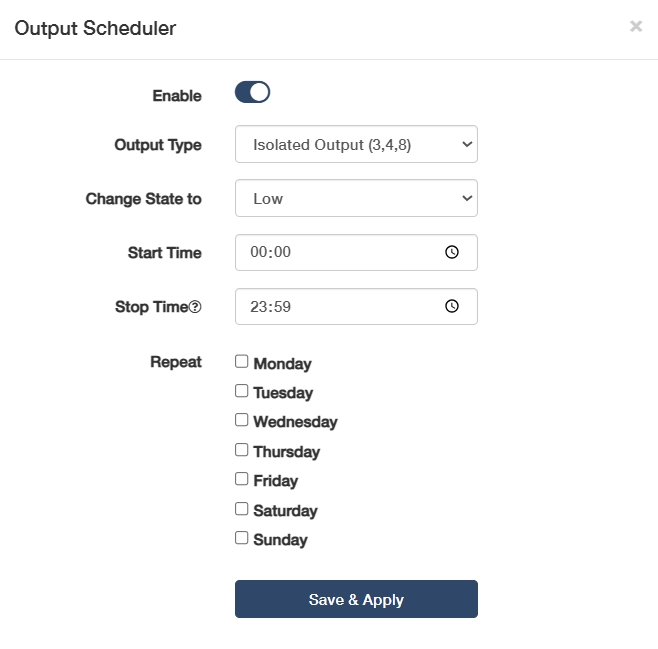
Output Type & Change State to: Select to define the target output and state.
◦ Isolated Output (3,4,8): Galvanically separated outputs for sensitive equipment, preventing ground loops in PLC/SCADA systems. Then select Change State to High for activating the optocoupler/solid-state relay to send the preset voltage to the connected device, or Low for cutting off output voltage to create an open circuit.
◦ Relay (5,10): Electromechanical contacts for switching high-power loads. Then select Change State to Closed for physically connecting the relay’s internal contacts to allow current flow, or Open for breaking the contact to stop current flow.
◦ Output (Power Socket 4): Direct mains power control for appliances, with built-in overload protection. Then select Change State to High for enabling mains power output, or Low for disconnecting mains power (safety cutoff).
-
Start Time: Set an exact activation time for a-new-day shift start.
- Stop Time: Set a deactivation time for end-of-day shutdown.
-
Repeat: Select specific weekdays for cyclical automation of the output schedule.
◦ Weekdays (Mon-Fri): Ideal for factory equipment schedules (e.g., conveyor activation at 08:00-17:00).
◦ Weekends (Sat-Sun): Used for non-routine operations (e.g., backup system tests).
◦ 7-Day Cycle: For 24/7 critical systems (e.g., server room cooling).